Introduction
Navigating the real estate market can be complex, whether you’re a first-time homebuyer, an experienced investor, or a homeowner looking to sell. To help you through the process, we’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions (FAQs) about real estate. This guide covers essential topics to ensure you’re well-informed and prepared for your real estate journey.
General Real Estate FAQs
1. What is Real Estate?
Real estate refers to land and any permanent structures attached to it, such as homes, buildings, or natural resources. It encompasses residential, commercial, industrial, and land properties.
2. Why is Location Important in Real Estate?
Location is crucial because it affects property value, accessibility, amenities, and future growth potential. A good location can enhance your property’s value over time.
3. What are the Different Types of Real Estate?
- Residential: Includes single-family homes, apartments, condos, and townhouses.
- Commercial: Comprises office buildings, retail spaces, and warehouses.
- Industrial: Involves factories, manufacturing plants, and logistics centers.
- Land: Refers to undeveloped land or land for agricultural use.
Home Buying FAQs
4. How Do I Start the Home Buying Process?
Begin by assessing your financial situation and obtaining a mortgage pre-approval. Next, find a reputable real estate agent and start exploring properties within your budget and desired location.
5. What is a Mortgage Pre-Approval?
A mortgage pre-approval is a document from a lender indicating how much they are willing to lend you based on your financial profile. It helps you understand your budget and shows sellers that you’re a serious buyer.
6. What Should I Look for When Viewing Homes?
Consider factors such as location, size, layout, condition, neighborhood amenities, and future resale value. It’s also essential to inspect for potential issues like structural damage or outdated systems.
7. What is the Role of a Real Estate Agent?
A real estate agent assists with property searches, negotiations, paperwork, and provides market insights. They act as your advocate throughout the buying or selling process.
Home Selling FAQs
8. How Do I Prepare My Home for Sale?
Start by decluttering, making necessary repairs, and enhancing curb appeal. Consider staging your home to make it more attractive to potential buyers. Professional photos and a well-written listing are also crucial.
9. How Do I Determine My Home’s Selling Price?
Work with your real estate agent to conduct a comparative market analysis (CMA), which evaluates similar properties in your area. Factors like location, condition, and market trends will influence the price.
10. What is the Best Time to Sell a House?
Spring and summer are traditionally the best times to sell, as the weather is favorable and buyers are more active. However, local market conditions and personal circumstances should also be considered.
11. What Costs Are Involved in Selling a Home?
Expect to pay for agent commissions, closing costs, repairs, staging, and potential moving expenses. These costs can vary, so discuss them with your agent to budget accordingly.
Real Estate Investment FAQs
12. What is Real Estate Investing?
Real estate investing involves purchasing properties to generate income or profit through rental income, property appreciation, or both. It can include residential, commercial, or industrial properties.
13. What are the Benefits of Real Estate Investing?
Benefits include potential for steady income, property appreciation, tax advantages, and portfolio diversification. Real estate can be a tangible asset with relatively stable long-term returns.
14. What are Common Real Estate Investment Strategies?
- Buy and Hold: Purchasing properties to rent out for ongoing income.
- Flipping: Buying properties, renovating them, and selling for a profit.
- BRRRR: Buy, Rehab, Rent, Refinance, Repeat – a strategy for building a portfolio.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): Investing in real estate through publicly traded companies.
15. How Do I Finance Real Estate Investments?
Options include traditional mortgages, private lenders, hard money loans, and partnerships. Your choice will depend on your investment strategy, creditworthiness, and financial goals.
Legal and Financial FAQs
16. What is a Real Estate Closing?
The closing is the final step in a real estate transaction where ownership transfers from the seller to the buyer. It involves signing documents, paying closing costs, and recording the deed.
17. What are Closing Costs?
Closing costs are fees associated with finalizing a real estate transaction. They can include appraisal fees, title insurance, attorney fees, and more. Buyers and sellers typically share these costs.
18. What is Title Insurance?
Title insurance protects against potential legal disputes over property ownership. It ensures that the property’s title is clear and that there are no outstanding claims or liens.
19. What is Escrow?
Escrow is a neutral third party that holds funds or documents until all conditions of a real estate transaction are met. It ensures both parties fulfill their obligations before the transaction is completed.
20. What is a Home Inspection?
A home inspection examines a property’s condition, usually conducted by a professional inspector. It identifies any issues or repairs needed before finalizing the purchase.
Mortgage and Financing FAQs
21. What is the Difference Between Fixed-Rate and Adjustable-Rate Mortgages?
- Fixed-Rate Mortgage: The interest rate remains constant throughout the loan term, providing predictable monthly payments.
- Adjustable-Rate Mortgage (ARM): The interest rate can change periodically based on market conditions, potentially leading to lower initial rates but variable future payments.
22. How Do I Choose the Right Mortgage Term?
Common mortgage terms are 15, 20, or 30 years. Shorter terms typically have higher monthly payments but lower total interest costs. Longer terms offer lower monthly payments but higher overall interest expenses. Choose based on your financial situation and long-term goals.
23. What is a Jumbo Loan?
A jumbo loan exceeds the conforming loan limits set by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA). It is used for high-value properties and typically has stricter credit requirements and higher interest rates.
24. What is Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI)?
PMI is insurance that lenders require when a borrower makes a down payment of less than 20%. It protects the lender in case of default but adds to the monthly mortgage cost. PMI can be canceled once the borrower reaches 20% equity.
25. How Do Interest Rates Affect My Mortgage?
Interest rates directly impact your monthly mortgage payments and the total cost of the loan. Lower rates reduce payments and overall costs, while higher rates increase them. It’s crucial to monitor market trends and lock in favorable rates when possible.
Legal and Regulatory FAQs
26. What is the Difference Between a Deed and a Title?
- Deed: A legal document that transfers ownership of property from one party to another.
- Title: The legal right to own, use, and control a property. It represents the ownership record.
27. What is a Real Estate Disclosure?
A disclosure is a document provided by the seller that outlines any known issues or defects with the property. It ensures transparency and informs buyers about potential problems before the purchase.
28. What is a Contingency in a Real Estate Contract?
A contingency is a condition that must be met for the contract to become binding. Common contingencies include financing, home inspection, and appraisal. If contingencies are not met, the buyer can withdraw without penalty.
29. How Do Zoning Laws Affect Property Use?
Zoning laws regulate land use and property development within specific areas. They determine what types of buildings are allowed, their sizes, and their purposes (e.g., residential, commercial, industrial). Compliance with zoning laws is essential for legal property use.
30. What is Eminent Domain?
Eminent domain is the government’s power to take private property for public use, with compensation to the owner. It is typically used for infrastructure projects like roads, schools, or utilities.
Market Trends and Analysis FAQs
31. How Do I Analyze Real Estate Market Trends?
Consider factors like property values, inventory levels, days on market, and economic indicators. Utilize tools like MLS (Multiple Listing Service), real estate websites, and market reports to gather data and identify trends.
32. What is a Seller’s Market vs. a Buyer’s Market?
- Seller’s Market: Demand exceeds supply, leading to higher prices and competitive bidding among buyers.
- Buyer’s Market: Supply exceeds demand, resulting in lower prices and more negotiating power for buyers.
33. How Do Interest Rates Impact the Real Estate Market?
Interest rates influence borrowing costs, buyer affordability, and overall market activity. Low rates can stimulate demand and increase property values, while high rates can slow the market and decrease prices.
34. What Are Real Estate Cycles?
Real estate cycles are phases of market activity, including expansion (growth), peak (high activity), contraction (decline), and trough (low activity). Understanding these cycles helps investors time their purchases and sales.
35. How Do Demographics Affect Real Estate Trends?
Demographics, such as population growth, age distribution, and household income, impact housing demand and preferences. Analyzing demographic trends can reveal emerging opportunities in specific markets.
Advanced Investment Strategies FAQs
36. What is Real Estate Syndication?
Real estate syndication involves pooling funds from multiple investors to purchase larger properties or portfolios. It allows investors to share risks and returns, and access deals they might not afford individually.
37. What is a 1031 Exchange?
A 1031 exchange allows investors to defer capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds from a sold property into a similar or “like-kind” property. It is a valuable strategy for growing and preserving real estate wealth.
38. How Do I Evaluate a Real Estate Investment?
Assess factors like location, property condition, rental income potential, expenses, and market trends. Use metrics such as capitalization rate, cash-on-cash return, and internal rate of return (IRR) to analyze profitability.
39. What is Real Estate Crowdfunding?
Real estate crowdfunding involves raising small amounts of capital from a large number of investors to fund real estate projects. It offers a way for smaller investors to participate in larger deals and diversify their portfolios.
40. What Are Opportunity Zones?
Opportunity Zones are designated areas that offer tax incentives for investments aimed at economic development and job creation. Investing in these zones can provide significant tax benefits, including deferrals and exclusions of capital gains.
Additional Resources and Tips
41. What Should I Look for in a Real Estate Agent?
Choose an agent with experience, local market knowledge, strong negotiation skills, and positive client reviews. A good agent can significantly impact your buying or selling experience.
42. How Do I Determine Property Value?
Use methods such as comparative market analysis (CMA), professional appraisals, and online valuation tools. Consider factors like location, condition, size, and recent sales of similar properties.
43. What is House Hacking?
House hacking involves buying a multi-unit property, living in one unit, and renting out the others to cover the mortgage and generate income. It’s a popular strategy for new investors to enter the real estate market.
44. How Can I Maximize Rental Income?
Optimize rental income by maintaining the property, setting competitive but fair rent prices, marketing effectively, and providing excellent tenant service. Consider short-term rentals or furnished rentals for higher returns.
45. What is the BRRRR Strategy?
BRRRR stands for Buy, Rehab, Rent, Refinance, Repeat. It’s a method for acquiring distressed properties, improving them, renting them out, refinancing to pull out equity, and repeating the process to build a portfolio.
Conclusion
This expanded FAQ guide aims to provide deeper insights into the complexities of real estate. By understanding these advanced topics, you can make more informed decisions and optimize your real estate ventures. For personalized advice or further questions, consult with experienced real estate professionals who can guide you through the process.
Why You Should Sell Your Deals with Us
Jorge Vazquez2025-08-02T03:43:24+00:00August 2nd, 2025|Comments Off on Why You Should Sell Your Deals with Us
Let’s keep it real—wholesaling ain’t easy. You lock up a deal, hustle to find a buyer, get ghosted five times, and by the time someone’s ready, the seller’s threatening to [...]
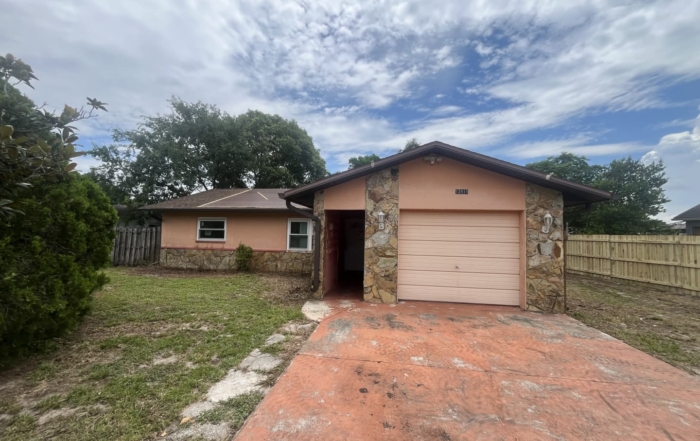
For Sale: 12914 Buckhorn Dr, Hudson, FL 34669
Jorge Vazquez2025-08-01T19:08:10+00:00August 1st, 2025|Comments Off on For Sale: 12914 Buckhorn Dr, Hudson, FL 34669
12914 Buckhorn Dr, Hudson, FL 34669 • Single Family • 3 Beds / 2 Baths • 1,542 sq ft living area [...]
Landlords, Listen Up: Florida’s A+ Economy Is Coming—Here’s Why 2025 Still Makes Sense
Jorge Vazquez2025-08-01T19:53:23+00:00July 31st, 2025|Comments Off on Landlords, Listen Up: Florida’s A+ Economy Is Coming—Here’s Why 2025 Still Makes Sense
Florida’s A+ Economy in 2026: What This Means for Landlords, Renters, and Real Investors Like Me By Jorge Vazquez, CEO of Graystone Investment Group In my 20 years of experience in real estate investing, [...]
What It Really Takes for Agents to Make Millions in Real Estate
Jorge Vazquez2025-08-01T01:32:51+00:00July 31st, 2025|Comments Off on What It Really Takes for Agents to Make Millions in Real Estate
What It Really Takes for Agents to Make Millions in Real Estate Inspired by a Fellow Featured Agent—Kat Palmiotti Something special happened recently—both Kat Palmiotti and I had our articles featured on ActiveRain's main [...]
Jorge Vazquez Featured on ActiveRain for Real Estate Insight
Jorge Vazquez2025-08-01T19:20:27+00:00July 31st, 2025|Comments Off on Jorge Vazquez Featured on ActiveRain for Real Estate Insight
Graystone Investment Group CEO Jorge Vazquez Featured on ActiveRain for Insightful Real Estate Blog Post FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Graystone CEO Jorge Vazquez Featured on ActiveRain for Viral Real Estate Blog [...]
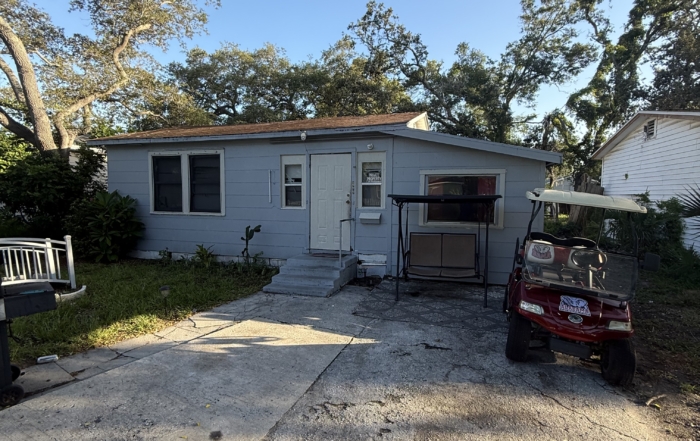
For Sale: 4717 11th Ave S, St. Petersburg, FL 33711
Jorge Vazquez2025-07-29T19:05:54+00:00July 29th, 2025|Comments Off on For Sale: 4717 11th Ave S, St. Petersburg, FL 33711
4717 11th Ave S, St. Petersburg, FL 33711 • Single Family Home [...]
Pick your expert. Book your free 15-minute consult now. We are here to help!
Our Top Articles
Why You Should Sell Your Deals with Us
Jorge Vazquez2025-08-02T03:43:24+00:00August 2nd, 2025|Comments Off on Why You Should Sell Your Deals with Us
Let’s keep it real—wholesaling ain’t easy. You lock up a deal, hustle to find a [...]
Landlords, Listen Up: Florida’s A+ Economy Is Coming—Here’s Why 2025 Still Makes Sense
Jorge Vazquez2025-08-01T19:53:23+00:00July 31st, 2025|Comments Off on Landlords, Listen Up: Florida’s A+ Economy Is Coming—Here’s Why 2025 Still Makes Sense
Florida’s A+ Economy in 2026: What This Means for Landlords, Renters, and Real Investors Like Me By Jorge Vazquez, [...]
What It Really Takes for Agents to Make Millions in Real Estate
Jorge Vazquez2025-08-01T01:32:51+00:00July 31st, 2025|Comments Off on What It Really Takes for Agents to Make Millions in Real Estate
What It Really Takes for Agents to Make Millions in Real Estate Inspired by a Fellow Featured Agent—Kat Palmiotti [...]
Property Profit Academy:
✔ Learn to buy properties with little to no money down.
✔ Build a $10M portfolio step by step.
✔ Master strategies like BRRRR and house hacking.